Which of the following provides the BEST description of a test case?
A) document specifying a sequence of actions for the execution of a test. Also known as test script or manual test script
B) A set of input values and expected results, with execution preconditions and execution postconditions, developed for a particular test condition
C) An attribute of a system specified by requirements documentation (for example reliability, usability or design constraints) that is executed in a test
D) An item or event of a system that could be verified by one or more test conditions, e.g., a function, transaction, feature, quality attribute, or structural element
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Based on definition of a test procedure specification. B. CORRECT – Based on definition from Glossary. C. INCORRECT – Based on Glossary definition of feature. D. INCORRECT – Based on definition of test condition, but replaced the term test case with test condition.
Which of the following is a major objective of testing?
- A) To prevent defects
- B) To validate the project plan works as required
- C) To gain confidence in the development team
- D) To make release decisions for the system under test
Justification
A. CORRECT – One of the major objectives of testing from the syllabus (1.1.1).
B. INCORRECT – Validation of the project plan would be a project management activity.
C. INCORRECT – Gaining confidence in the development team would be achieved through observation and experience.
D. INCORRECT – One of the main objectives during acceptance testing may be to give information to stakeholders about the risk of releasing the system at a given time – so testing provides information for stakeholders to make decisions, it does not provide the release decision.
Which of the following is an example of a failure in a car cruise control system?
-
A) The developer of the system forgot to rename variables after a cut-and-paste operation
-
B) Unnecessary code that sounds an alarm when reversing was included in the system
-
C) The system stops maintaining a set speed when the radio volume is increased or decreased
-
D) The design specification for the system wrongly states speeds in km/h
Justification
A. INCORRECT – This is an example of a mistake made by the developer.
B. INCORRECT – This is an example of a defect (something wrong in the code that may cause a failure).
C. CORRECT – This is a deviation from the expected functionality - a cruise control system should not be affected by the radio.
D. INCORRECT – This is an example of a defect (something wrong in a specification that may cause a failure if subsequently implemented).
Which of the following is a defect rather than a root cause (in a fitness tracker)?
-
A) Because he was unfamiliar with the domain of fitness training, the author of the requirements wrongly assumed that users wanted heartbeat in beats per hour
-
B) The tester of the smartphone interface had not been trained in state transition testing, so missed a major defect
-
C) An incorrect configuration variable included for the GPS function could cause location problems during daylight saving times
-
D) Because she had never worked on wearable devices before, the designer of the user interface misunderstood the effects of reflected sunlight
Justification
A. INCORRECT – The lack of familiarity of the requirements author with the fitness domain is a root cause.
B. INCORRECT – The lack of training of the tester in state transition testing was one of the root causes of the defect (the developer presumably created the defect, as well).
C. CORRECT – The incorrect configuration data represents faulty software in the fitness tracker (a defect), that may cause failures.
D. INCORRECT – The lack of experience in designing user interfaces for wearable devices is a typical example of a root cause of a defect.
As a result of risk analysis, more testing is being directed to those areas of the system under test where initial testing found more defects than average. Which of the following testing principles is being applied?
-
A) Beware of the pesticide paradox
-
B) Testing is context dependent
-
C) Absence-of-errors is a fallacy
-
D) Defects cluster together
Justification
A. INCORRECT – ‘Beware of the pesticide paradox’ is concerned with re-running the same tests and their fault-finding effectiveness decreasing.
B. INCORRECT – This testing principle is concerned with performing testing differently based on the context (e.g. games vs safety-critical).
C. INCORRECT – This testing principle is concerned with the difference between a tested and fixed system and a validated system. No ‘errors’ does not mean the system is fit for use.
D. CORRECT – If clusters of defects are identified (areas of the system containing more defects than average), then testing effort should be focused on these areas.
Given the following test activities and tasks:
-
a. Test design
-
b. Test implementation
-
c. Test execution
-
d. Test completion
-
Entering change requests for open defect reports
-
Identifying test data to support the test cases
-
Prioritizing test procedures and creating test data
-
Analyzing discrepancies to determine their cause
Which of the following BEST matches the activities with the tasks?
Justification
The correct pairing of test activities and tasks, according to the syllabus (1.4.2) is:
a. Test design – (2) Identifying test data to support the test cases
b. Test implementation – (3) Prioritizing test procedures and creating test data
c. Test execution – (4) Analyzing discrepancies to determine their cause
d. Test completion – (1) Entering change requests for open defect reports
Thus, option A is CORRECT
Which of the following BEST describes how value is added by maintaining traceability between the test basis and test artifacts?
-
A. Maintenance testing can be fully automated based on changes to the initial requirements
-
B. It is possible to determine if a new test case has increased coverage of the requirements
-
C. Test managers can identify which testers found the highest severity defects
-
D. Areas that may be impacted by side-effects of a change can be targeted by confirmation testing
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Traceability will allow existing test cases to be linked with updated and deleted requirements (although there will be no support for new requirements), but it will not help with the automation of maintenance testing.
B. CORRECT – If all test cases are linked with requirements, then whenever a new test case (with traceability) is added, it is possible to see if any previously-uncovered requirements are covered by the new test case.
C. INCORRECT – Traceability between the test basis and test artifacts will not provide information on which testers found high-severity defects, and, even if this information could be determined, it would be of limited value.
D. INCORRECT – Traceability can help with identifying test cases affected by changes, however areas impacted by side-effects would be the focus of regression testing.
Which of the following qualities is MORE likely to be found in a tester than in a developer?
-
A. Experience on which to base their efforts
-
B. Ability to see what might go wrong
-
C. Good communication with team members
-
D. Attention to detail
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Both developers and testers gain from experience.
B. CORRECT – Developers are often more interested in designing and building solutions than in contemplating what might be wrong with those solutions.
C. INCORRECT – Both developers and testers should be able to communicate well.
D. INCORRECT – Both developers and testers need to pay attention to detail
Given the following statements about the relationships between software development activities and test activities in the software development lifecycle:
-
Each development activity should have a corresponding testing activity
-
Reviewing should start as soon as final versions of documents become available
-
The design and implementation of tests should start during the corresponding development activity
-
Testing activities should start in the early stages of the software development lifecycle
Which of the following CORRECTLY shows which are true and false?
-
A. True – 1, 2; False – 3, 4
-
B. True – 2, 3; False – 1, 2
-
C. True – 1, 2, 4; False – 3
-
D. True – 1, 4; False – 2, 3
Justification
Considering each statement:
-
Each development activity should have a corresponding testing activity. TRUE – as described in the syllabus (2.1.1).
-
Reviewing should start as soon as final versions of documents become available. FALSE – it should start as soon as drafts are available, as per syllabus (2.1.1).
-
The design and implementation of tests should start during the corresponding development activity. FALSE – the analysis and design of tests should start during the corresponding development activity, not the implementation, as per syllabus (2.1.1).
-
Testing activities should start in the early stages of the software development lifecycle. TRUE - as described in the syllabus (2.1.1).
Thus, option D is CORRECT
Given that the testing being performed has the following attributes:
• based on interface specifications;
• focused on finding failures in communication;
• the test approach uses both functional and structural test types.
Which of the following test levels is MOST likely being performed?
A. Component integration testing
B. Acceptance testing
C. System testing
D. Component testing
Justification
Considering the scenario and the syllabus (2.2):
• ‘testing is based on interface specifications’ – the test basis for component integration testing includes interface specifications (along with communication protocol specification), while these are not included for any of the other test levels
• ‘testing is focused on finding failures in communication’ - failures in the communication between tested components is included as a typical failure for component integration testing, but failures in communication is not included for any of the other test levels
• ‘the test approach uses both functional and structural test types’ - functional and structural test types are both included as possible approaches for component integration testing, and would also be appropriate for any of the other test levels, although they are only otherwise explicitly mentioned in the syllabus for system testing
Thus, option A is CORRECT.
Which of the following statements about test types and test levels is CORRECT?
-
A. Functional and non-functional testing can be performed at system and acceptance test levels, while white-box testing is restricted to component and integration testing
-
B. Functional testing can be performed at any test level, while white-box testing is restricted to component testing
-
C. It is possible to perform functional, non-functional and white-box testing at any test level
-
D. Functional and non-functional testing can be performed at any test level, while white-box testing is restricted to component and integration testing
Justification
A. INCORRECT – It is possible to perform any of the test types (functional, non-functional, white-box) at any test level - so, although it is correct that functional and non-functional testing can be performed at system and acceptance test levels, it is incorrect to state that white-box testing is restricted to component and integration testing.
B. INCORRECT – It is possible to perform any of the test types (functional, non-functional, white-box) at any test level - so, it is incorrect to state that white-box testing is restricted to component testing.
C. CORRECT – It is possible to perform any of the test types (functional, non-functional, white-box) at any test level.
D. INCORRECT – It is possible to perform any of the test types (functional, non-functional, white-box) at any test level - so, it is incorrect to state that white-box testing is restricted to component testing and integration testing.
Which of the following statements BEST compares the purposes of confirmation testing and regression testing?
-
A. The purpose of regression testing is to ensure that all previously run tests still work correctly, while the purpose of confirmation testing is to ensure that any fixes made to one part of the system have not adversely affected other parts
-
B. The purpose of confirmation testing is to check that a previously found defect has been fixed, while the purpose of regression testing is to ensure that no other parts of the system have been adversely affected by the fix
-
C. The purpose of regression testing is to ensure that any changes to one part of the system have not caused another part to fail, while the purpose of confirmation testing is to check that all previously run tests still provide the same results as before
-
D. The purpose of confirmation testing is to confirm that changes to the system were made successfully, while the purpose of regression testing is to run tests that previously failed to ensure that they now work correctly
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Although the description of regression testing is largely correct, the description of confirmation testing (which should be testing a defect has been fixed) is not correct.
B. CORRECT – The descriptions of both confirmation and regression testing match the intent of those in the syllabus.
C. INCORRECT – Although the description of regression testing is largely correct, the description of confirmation testing (re-running all previously run tests to get the same results) is not correct, as the purpose of confirmation testing is to check that tests that previously failed now pass (the fix worked).
D. INCORRECT – Although the description of confirmation testing is largely correct, the description of regression testing (re-running tests that previously failed) is not correct (this is a more detailed description of confirmation testing).
Which of the following statements CORRECTLY describes a role for impact analysis in maintenance?
-
A. Impact analysis is used when deciding if a fix to a maintained system is worthwhile
-
B. Impact analysis is used to identify how data should be migrated into the maintained system
-
C. Impact analysis is used to decide which hot fixes are of most value to the user
-
D. Impact analysis is used to determine the effectiveness of new maintenance test
cases
Justification
A. CORRECT – Impact analysis may be used to identify those areas of the system that will be affected by the fix, and so the extent of the impact (e.g. necessary regression testing) can be used when deciding if the change is worthwhile, as per syllabus (2.4.2).
B. INCORRECT – Although testing migrated data is part of maintenance testing (see conversion testing), impact analysis does not identify how this is done.
C. INCORRECT – Impact analysis shows which parts of a system are affected by a change, so it can show the difference between different hot fixes in terms of the impact on the system, however it does not give any indication of the value of the changes to the user.
D. INCORRECT – Impact analysis shows which parts of a system are affected by a change, it cannot provide an indication of the effectiveness of test cases.
Which of the following statements CORRECTLY reflects the value of static testing?
-
A. By introducing reviews, we have found that both the quality of specifications and the time required for development and testing have increased
-
B. Using static testing means we have better control and cheaper defect management due to the ease of removing defects later in the lifecycle
-
C. Now that we require the use of static analysis, missed requirements have decreased and communication between testers and developers has improved
-
D. Since we started using static analysis, we have found coding faults that we would not have found by only performing dynamic testing
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Reviews should increase the quality of specifications, however the time required for development and testing should decrease, as per syllabus (3.1.2).
B. INCORRECT – Removing defects is generally easier earlier in the life cycle, as per syllabus (3.1.2).
C. INCORRECT – Reviews will result in fewer missed requirements and better communication between testers and developers, however this is not true of static analysis, as per syllabus (3.1.2).
D. CORRECT – This is a benefit of static analysis, as per syllabus (3.1.2).
Which of the following sequences BEST shows the main activities of the work product review process?
-
A. Initiate review – Reviewer selection – Individual review – Issue communication and analysis – Rework
-
B. Planning & preparation – Overview meeting – Individual review – Fix– Report
-
C. Preparation – Issue detection – Issue communication and analysis – Rework – Report
-
D. Plan – Initiate review – Individual review – Issue communication and analysis – Fix defects & report
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Reviewer selection is not one of the main activities for the work product review process in the syllabus (3.2.1).
B. INCORRECT – This is a possible set of activities for a work product review process, but it is missing the ‘Issue communication and analysis’ activity, and it does not match the main activities for the work product review process in the syllabus (3.2.1).
C. INCORRECT – This is a possible set of activities for a work product review process, but it is missing the ‘initiate review’ activity, and it does not match the main activities for the work product review process in the syllabus (3.2.1).
D. CORRECT – This is the order of the activities as provided in the syllabus (3.2.1).
Which of the following CORRECTLY matches the roles and responsibilities in a formal review?
-
A. Manager – Decides on the execution of reviews
-
B. Review Leader - Ensures effective running of review meetings C. Scribe – Fixes defects in the work product under review
-
D. Moderator – Monitors ongoing cost-effectiveness
Justification
A. CORRECT – As stated in the syllabus (3.2.2).
B. INCORRECT – The moderator should ensure the effective running of review meetings, as per syllabus (3.2.2).
C. INCORRECT – The author fixes the work product under review, as per syllabus (3.2.2).
D. INCORRECT – The manager monitors ongoing cost-effectiveness, as per syllabus (3.2.2)
The reviews being used in your organization have the following attributes:
• There is a role of a scribe
• The purpose is to detect potential defects
• The review meeting is led by the author
• Reviewers find potential defects by individual review
• A review report is produced Which of the following review types is MOST likely being used?
-
A. Informal Review
-
B. Walkthrough
-
C. Technical Review
-
D. Inspection
Justification
Considering the attributes and the syllabus (3.2.3):
• There is a role of a scribe – specified for walkthroughs, technical reviews and inspections; thus, the reviews being performed cannot be informal reviews.
• The purpose is to detect potential defects – the purpose of detecting potential defects is specified for all types of review.
• The review meeting is led by the author – this is not allowed for inspections and is typically not the author for technical reviews, but is part of walkthroughs, and allowed for informal reviews
• Reviewers find potential issues by individual review all types of reviews can include individual review (even informal reviews) • A review report is produced - all types of reviews can produce a review report, although it would be less likely for an informal review.
Thus, option B is CORRECT.
You have been asked to take part in a checklist-based review of the following excerpt from the requirements specification for a library system:
Librarians can:
- Register new borrowers.
- Return books from borrowers.
- Accept fines from borrowers.
- Add new books to the system with their ISBN, author and title.
- Remove books from the system.
- Get system responses within 5 seconds.
Borrowers can: 7. Borrow a maximum of 3 books at one time. 8. View the history of books they have borrowed/reserved. 9. Be fined for failing to return a book within 3 weeks. 10. Get system responses within 3 seconds. 11. Borrow a book at no cost for a maximum of 4 weeks. 12. Reserve books (if they are on-loan).
All users (librarians and borrowers): 13. Can search for books by ISBN, author, or title. 14. Can browse the system catalogue. 15. The system shall respond to user requests within 3 seconds. 16. The user interface shall be easy-to-use. You have been assigned the checklist entry that requires you to review the specification for inconsistencies between individual requirements (i.e. conflicts between requirements).
Which of the following CORRECTLY identifies inconsistencies between pairs of requirements?
A. 6-10, 6-15, 7-12 B. 6-15, 9-11 C. 6-10, 6-15, 9-11 D. 6-15, 7-12
Justification
Considering the potential inconsistencies:
• 6-10 – If librarians should get system responses within 5 seconds, it is NOT inconsistent for borrowers to get system responses within 3 seconds.
• 6-15 - If librarians should get system responses within 5 seconds, it is inconsistent for all users to get system responses within 3 seconds.
• 7-12 – If borrowers can borrow a maximum of 3 books at one time it is NOT inconsistent for them to also reserve books (if they are on-loan).
• 9-11 – If a borrower can be fined for failing to return a book within 3 weeks it is inconsistent for them to also be allowed to borrow a book at no cost for a maximum of 4 weeks – as the length of valid loans are different.
Thus, of the potential inconsistencies, 6-15 and 9-11 are valid inconsistencies, and so option B is CORRECT
Which of the following provides the BEST description of exploratory testing?
-
A. A testing practice in which an in-depth investigation of the background of the test object is used to identify potential weaknesses that are examined by test cases
-
B. An informal test design technique where the tester actively controls the design of the tests as those tests are performed and uses information gained while testing to design new and better tests
-
C. An approach to test design in which test activities are planned as uninterrupted sessions of test analysis and design, often used in conjunction with checklist-based testing
-
D. Testing based on the tester's experience, knowledge and intuition
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Exploratory testing is often carried out when timescales are short, so making in-depth investigations of the background of the test object is unlikely.
B. CORRECT – Glossary definition.
C. INCORRECT – based on the Glossary definition of session-based testing, but with test execution replaced by test analysis.
D. INCORRECT – Glossary definition of experience-based testing.
Which of the following BEST matches the descriptions with the different categories of test techniques?
-
Coverage is measured based on a selected structure of the test object
-
The processing within the test object is checked
-
Tests are based on likely defects and their distribution
-
Deviations from the requirements are checked
-
User stories are used as the test basis
Black - Black-box test techniques White - White-box test techniques Experience - Experience-based test techniques
A. Black – 4, 5 White – 1, 2 Experience – 3
B. Black – 3 White – 1, 2 Experience – 4, 5
C. Black – 4 White – 1, 2 Experience – 3, 5
D. Black – 1, 3, 5 White – 2 Experience – 4
Justification
The correct pairing of descriptions with the different categories of test techniques, according to the syllabus (4.1.1) is:
Black-box test techniques Deviations from the requirements are checked (4) User stories are used as the test basis (5)
White-box test techniques Coverage is measured based on a selected structure of the test object (1) The processing within the test object is checked (2)
Experience-based test techniques Tests are based on likely defects and their distribution (3)
Thus, option A is CORRECT.
A fitness app measures the number of steps that are walked each day and provides feedback to encourage the user to keep fit.
The feedback for different numbers of steps should be:
Up to 1000 - Couch Potato! Above 1000, up to 2000 - Lazy Bones! Above 2000, up to 4000 - Getting There! Above 4000, up to 6000 - Not Bad! Above 6000 - Way to Go!
Which of the following sets of test inputs would achieve the highest equivalence partition coverage?
-
A. 0, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000
-
B. 1000, 2001, 4000, 4001, 6000
-
C. 123, 2345, 3456, 4567, 5678
-
D. 666, 999, 2222, 5555, 6666
Justification
The following valid equivalence partitions can be identified:
(1) Up to 1000 - Couch Potato! (2) Above 1000, up to 2000 - Lazy Bones! (3) Above 2000, up to 4000 - Getting There! (4) Above 4000, up to 6000 - Not Bad! (5) Above 6000 - Way to Go!
The sets of test inputs therefore cover the following partitions:
A. 0 (1), 1000 (1), 2000 (2), 3000 (3), 4000 (3) – 3 partitions (out of 5)
B. 1000 (1), 2001 (3), 4000 (3), 4001 (4), 6000 (4) – 3 partitions (out of 5)
C. 123 (1), 2345 (3), 3456 (3), 4567 (4), 5678 (4) – 3 partitions (out of 5)
D. 666 (1), 999 (1), 2222 (3), 5555 (4), 6666 (5) – 4 partitions (out of 5)
Thus, option D is CORRECT
A daily radiation recorder for plants produces a sunshine score based on a combination of the number of hours a plant is exposed to the sun (below 3 hours, 3 to 6 hours or above 6 hours) and the average intensity of the sunshine (very low, low, medium or high).
Given the following test cases:
| | hours | intensity | score |
| T1 | 1.5 | v. low | 10 |
| T2 | 7.0 | medium | 60 |
| T3 | 0.5 | v.low | 10 |
What is the minimum number of additional test cases that are needed to ensure full coverage of all valid INPUT equivalence partitions?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Justification
The following valid input equivalence partitions can be identified:
hours
(1) below 3 hours (2) 3 to 6 hours (3) above 6 hours
intensity
(4) very low (5) low (6) medium (7) high
The given test cases cover the following valid input equivalence partitions:
T1 1.5 (1) v. low (4)
T2 7.0 (3) medium (6)
T3 0.5 (1) v. low (4)
Thus, the missing valid input equivalence partitions are: (2), (5) and (7). These can be covered by two test cases, as (2) can be combined with either(5) or (7).
Thus, option B is CORRECT.
A smart home app measures the average temperature in the house over the previous week and provides feedback to the occupants on their environmental-friendliness based on this temperature.
The feedback for different average temperature ranges (to the nearest °C) should be:
Up to 10°C - Icy Cool! 11°C to 15°C - Chilled Out! 16°C to 19°C - Cool Man! 20°C to 22°C - Too Warm! Above 22°C - Hot & Sweaty!
Using two-point BVA, which of the following sets of test inputs provides the highest level of boundary coverage?
A. 0°C, 11°C, 20°C, 22°C, 23°C
B. 9°C, 15°C, 19°C, 23°C, 100°C
C. 10°C, 16°C, 19°C, 22°C, 23°C
D. 14°C, 15°C, 18°C, 19°C, 21°C, 22°C
Justification
The input equivalence partitions, with two-point boundary values, can be represented as: The number of boundary values covered by the test inputs is therefore:
A. 0°C, 11°C, 20°C, 22°C, 23°C > 4 (11, 20, 22 and 23)
B. 9°C, 15°C, 19°C, 23°C, 100°C > 3 (15, 19 and 23)
C. 10°C, 16°C, 19°C, 22°C, 23°C > 5 (10, 16, 19, 22 and 23)
D. 14°C, 15°C, 18°C, 19°C, 21°C, 22°C > 3 (15, 19 and 22)
Thus, option C is CORRECT.
Decision table testing is being performed on a speeding fine system. Two test cases have already been generated for rules 1 and 4, which are shown below:
| RULES | R1 | R4 |
| Speed > 50 | T | F |
| School Zone | T | F |
| $250 Fine | F | F |
| Jail | T | F |
Given the following additional test cases:
| RULES | DT1 | TD2 | TD3 | TD4 |
| Speed | 55 | 44 | 66 | 77 |
| School Zone | T | T | T | F |
| $250 Fine | F | F | F | T |
| Jail | T | F | T | F |Which two of the additional test cases would achieve full coverage of the complete decision table (when combined with the test cases that have already been generated for rules 1 and 4)?
-
A. DT1, DT2
-
B. DT2, DT3
-
C. DT2, DT4
-
D. DT3, DT4
Justification
To achieve full coverage, test cases covering rules 2 and 3 are needed. DT4 satisfies the constraints of rule 2, while DT2 satisfies the constraints of rule 3. Thus, option C is CORRECT.
Given the following state model of battery charger software:
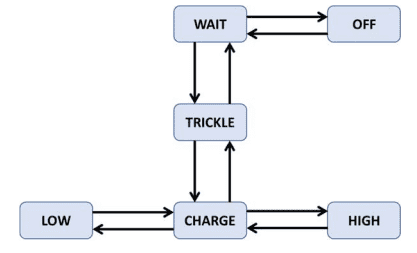
Which of the following sequences of transitions provides the highest level of transition coverage for the model?
-
A. OFF > WAIT > OFF > WAIT > TRICKLE > CHARGE > HIGH > CHARGE > LOW
-
B. WAIT > TRICKLE > WAIT > OFF > WAIT > TRICKLE > CHARGE > LOW > CHARGE
-
C. HIGH > CHARGE > LOW > CHARGE > TRICKLE > WAIT > TRICKLE > WAIT > TRICKLE > CHARGE
-
D. WAIT > TRICKLE > CHARGE > HIGH > CHARGE > TRICKLE > WAIT > OFF > WAIT
Justification
The options achieve the following transition coverage:
-
A. OFF (2) WAIT (1) OFF (2) WAIT (3) TRICKLE (5) CHARGE (9) HIGH (10) CHARGE (7) LOW = 7 transitions (out of 10)
-
B. WAIT (3) TRICKLE (4) WAIT (1) OFF (2) WAIT (3) TRICKLE (5) CHARGE (7) LOW (8) CHARGE = 7 transitions (out of 10)
-
C. HIGH (10) CHARGE (7) LOW (8) CHARGE (6) TRICKLE (4) WAIT (3) TRICKLE (4) WAIT (3) TRICKLE (5) CHARGE = 7 transitions (out of 10)
-
D. WAIT (3) TRICKLE (5) CHARGE (9) HIGH (10) CHARGE (6) TRICKLE (4) WAIT (1) OFF (2) WAIT = 8 transitions (out of 10)
Thus, option D is CORRECT
Which of the following statements BEST describes how test cases are derived from a use case?
-
A. Test cases are created to exercise defined basic, exceptional and error behaviors performed by the system under test in collaboration with actors
-
B. Test cases are derived by identifying the components included in the use case, and creating integration tests that exercise the interactions of these components
-
C. Test cases are generated by analyzing the interactions of the actors with the system to ensure the user interfaces are easy to use
-
D. Test cases are derived to exercise each of the decision points in the business process flows of the use case, to achieve 100% decision coverage of these flows
Justification
- A. CORRECT – The syllabus (4.2.5) explains that each use case specifies some
behavior that a subject can perform in collaboration with one or more actors. It also (later) explains that tests are designed to exercise the defined behaviors (basic, exceptional and errors).
- B. INCORRECT – Use cases normally specify requirements, and so do not ‘include’ the
components that will implement them.
- C. INCORRECT – Tests based on use cases do exercise interactions between the actor
and the system, but they are focused on the functionality and do not consider the ease of use of user interfaces.
- D. INCORRECT – Tests do cover the use case paths through the use case, but there is
no concept of decision coverage of these paths, and certainly not of business process flows
Which of the following descriptions of statement coverage is CORRECT?
-
A. Statement coverage is a measure of the number of lines of source code (minus comments) exercised by tests
-
B. Statement coverage is a measure of the proportion of executable statements in the source code exercised by tests
-
C. Statement coverage is a measure of the percentage of lines of source code exercised by tests
-
D. Statement coverage is a measure of the number of executable statements in the source code exercised by tests
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Statement coverage is a measure of the proportion of executable statements exercised. The number of executable statements is often close to the number of lines of code minus the comments, but this option only talks about the number of lines of code exercised and not the proportion exercised.
B. CORRECT – Statement coverage is a measure of the proportion of executable statements exercised (normally presented as a percentage), per syllabus (4.3.1).
C. INCORRECT – Statement coverage is a measure of the percentage of executable statements exercised, however many of the lines of source code are not executable (e.g. comments).
D. INCORRECT – Statement coverage is a measure of the proportion of executable statements exercised. This option only talks about the number of executable statements exercised and not the proportion (or percentage) exercised
Which of the following descriptions of decision coverage is CORRECT?
-
A. Decision coverage is a measure of the percentage of possible paths through the source code exercised by tests
-
B. Decision coverage is a measure of the percentage of business flows through the component exercised by tests
-
C. Decision coverage is a measure of the ‘if’ statements in the code that are exercised with both the true and false outcomes
-
D. Decision coverage is a measure of the proportion of decision outcomes in the source code exercised by tests
Justification
A. INCORRECT – A path through source code is one potential route through the code from the entry point to the exit point that could exercise a range of decision outcomes. Two different paths may exercise all but one of the same decision outcomes, and by just changing a single decision outcome a new path is followed. Test cases that would achieve decision coverage are typically a tiny subset of the test cases that would achieve path coverage. In practice, most non-trivial programs (and all programs with unconstrained loops, such as ‘while’ loops) have a potentially infinite number of possible paths through them and so measuring the percentage covered is practically infeasible.
B. INCORRECT – Coverage of business flows can be a focus of use case testing, but use cases rarely cover a single component. It may be possible to cover the decisions within business flows, but only if they were specified in enough detail, however this option only suggests coverage of business flows as a whole.
C. INCORRECT – Achieving full decision coverage does require all ‘if’ statements to be exercised with both true and false outcomes, however, there are typically several other decision points in the code (e.g. ‘case’ statements and the code controlling loops) that also need to be taken into consideration when measuring decision coverage.
D. CORRECT – Decision coverage is a measure of the proportion of decision outcomes exercised (normally presented as a percentage), as per syllabus (4.3.2).
Which of the following BEST describes the concept behind error guessing?
-
A. Error guessing requires you to imagine you are the user of the test object and guess mistakes the user could make interacting with it
-
B. Error guessing involves using your personal experience of development and the mistakes you made as a developer
-
C. Error guessing involves using your knowledge and experience of defects found in the past and typical mistakes made by developers
-
D. Error guessing requires you to rapidly duplicate the development task to identify the sort of mistakes a developer might make
Justification
A. INCORRECT – error guessing is not a usability technique for guessing how users may fail to interact with the test object.
B. INCORRECT – Although a tester who used to be a developer may use their personal experience to help them when performing error guessing, the technique is not based on prior knowledge of development.
C. CORRECT – The basic concept behind error guessing is that the tester tries to guess what mistakes may have been made by the developer and what defects may be in the test object based on past experience (and sometimes checklists).
D. INCORRECT – Duplicating the development task has several flaws that make it impractical, such as the requirement for the tester to have equivalent skills to the developer and the time involved in performing the development. It is not error guessing.
Which of the following BEST explains a benefit of independent testing?
-
A. The use of an independent test team allows project management to assign responsibility for the quality of the final deliverable to the test team,so ensuring everyone is aware that quality is the test team’s overall responsibility
-
B. If a test team external to the organization can be afforded, then there are distinct benefits in terms of this external team not being so easily swayed by the delivery concerns of project management and the need to meet strict delivery deadlines
-
C. An independent test team can work totally separately from the developers, need not be distracted with changing project requirements, and can restrict communication with the developers to defect reporting through the defect management system
-
D. When specifications contain ambiguities and inconsistencies, assumptions are made on their interpretation, and an independent tester can be useful in questioning those assumptions and the interpretation made by the developer
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Quality should be the responsibility of everyone working on the project and not the sole responsibility of the test team.
B. INCORRECT – First, it is not a benefit if an external test team does not meet delivery deadlines, and second, there is no reason to believe that external test teams will feel they do not have to meet strict delivery deadlines.
C. INCORRECT – It is bad practice for the test team to work in complete isolation, and we would expect an external test team to be concerned with changing project requirements and communicate well with developers.
D. CORRECT – Specifications are never perfect, meaning that assumptions will have to be made by the developer. An independent tester is useful in that they can challenge and verify the assumptions and subsequent interpretation made by the developer.
Which of the following tasks is MOST LIKELY to be performed by the test manager?
-
A. Write test summary reports based on the information gathered during testing
-
B. Review tests developed by others
-
C. Create the detailed test execution schedule
-
D. Analyze, review, and assess requirements, specifications and models for testability
Justification
A. CORRECT – One of the typical tasks of a test manager from the syllabus (5.1.2).
B. INCORRECT – One of the typical tasks of a tester from the syllabus (5.1.2).
C. INCORRECT – One of the typical tasks of a tester from the syllabus (5.1.2).
D. INCORRECT – One of the typical tasks of a tester from the syllabus (5.1.2).
Given the following examples of entry and exit criteria:
-
The original testing budget of $30,000 plus contingency of $7,000 has been spent
-
96% of planned tests for the drawing package have been executed and the remaining tests are now out of scope
-
The trading performance test environment has been designed, set-up and verified
-
There are now no outstanding critical defects and two high-priority defects
-
The autopilot design specifications have been reviewed and reworked
-
The tax rate calculation component has passed unit testing
Which of the following BEST categorizes them as entry and exit criteria:
A. Entry criteria – 5, 6 Exit criteria – 1, 2, 3, 4
B. Entry criteria – 2, 3, 6 Exit criteria – 1, 4, 5
C. Entry criteria – 1, 3 Exit criteria – 2, 4, 5, 6
D. Entry criteria – 3, 5, 6 Exit criteria – 1, 2, 4
Justification
The correct pairings of examples to entry and exit criteria are:
Entry criteria
• (3) The trading performance test environment has been designed, set-up and verified – example of the need for a test environment to be ready before testing can begin.
• (5) The autopilot design specifications have been reviewed and reworked – example of the need for the test basis to be available before testing can begin
• (6) The tax rate calculation component has passed unit testing – example of the need for a test object to have met the exit criteria for a prior level of testing before testing can begin.
Exit criteria
• (1) The original testing budget of $30,000 plus contingency of $7,000 has been spent – example of spending the testing budget being a signal to stop testing.
• (2) 96% of planned tests for the drawing package have been executed and the remaining tests are now out of scope – example of all the planned tests being run being a signal to stop testing (normally used alongside the exit criteria on outstanding defects remaining).
• (4) There are now no outstanding critical defects and two high-priority defects – example of the number of outstanding defects achieving a planned limit being a signal to stop testing (normally used alongside the exit criteria on planned tests being run).
Thus, option D is CORRECT.
Given the following priorities and dependencies for these test cases:
| t.case | priority | Technical dependent on | Logical dependent on |
| T1 | High | TC4 | |
| T2 | Low | | |
| T3 | High | | TC4 |
| T4 | Medium | | |
| T5 | Low | | TC2 |
| T6 | Medium | TC5 | |
Which of the following test execution schedules BEST takes into account the priorities and technical and logical dependencies?
-
A. TC1 – TC3 – TC4 – TC6 – TC2 – TC5
-
B. TC4 – TC3 – TC1 – TC2 – TC5 – TC6
-
C. TC4 – TC1 – TC3 – TC5 – TC6 – TC2
-
D. TC4 – TC2 – TC5 – TC1 – TC3 – TC6
Justification
The test cases should be scheduled in priority order, but the schedule must also take account of the dependencies. The two highest priority test cases (TC1 and TC3) are both dependent on TC4, so the first three test cases should be scheduled as either TC4 – TC1 – TC3 or TC4 – TC3 – TC1 (we have no way to discriminate between TC1 and TC3). Next, we need to consider the remaining medium priority test case, TC6. TC6 is dependent on TC5, but TC5 is dependent on TC2, so the next two three cases must be scheduled as TC2 - TC5 – TC6.
This means there are two possible optimal schedules:
• TC4 – TC1 – TC3 – TC2 - TC5 – TC6 or
• TC4 – TC3 – TC1 – TC2 - TC5 – TC6
Thus, option B is CORRECT.
Which of the following statements about test estimation approaches is CORRECT?
-
A. With the metrics-based approach, the estimate is based on test measures from the project and so this estimate is only available after the testing starts
-
B. With the expert-based approach, a group of expert users identified by the client recommends the necessary testing budget
-
C. With the expert-based approach, the test leads responsible for the different testing activities predict the expected testing effort
-
D. With the metrics-based approach, an average of the testing costs recorded from several past projects is used as the testing budget
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Estimates may be updated as more information becomes available, but estimates are needed to assist with planning before the testing starts.
B. INCORRECT – In the expert-based approach, the experts need to be experts in testing, not in using the test object.
C. CORRECT – Test leads, who will be leading testers doing the testing, are considered experts in their respective areas and suitable for estimating the necessary resources needed.
D. INCORRECT – While it is useful to know the testing costs from previous projects, a more sophisticated approach is needed than simply taking an average of past projects (the new project may not be similar to the previous projects, e.g. it may be far larger or far smaller than previous projects).
Which of the following BEST defines risk level?
-
A. Risk level is calculated by adding together the probabilities of all problem situations and the financial harm that results from them
-
B. Risk level is estimated by multiplying the likelihood of a threat to the system by the chance that threat will occur and lose money
-
C. Risk level is determined by a combination of the probability of an undesirable event and the expected impact of that event
-
D. Risk level is the sum of all potential hazards to a system multiplied by the sum of all potential losses from that system
Justification
A. INCORRECT – Risk is determined by considering a combination of the likelihood of problem situations and the harm that may result from them, but cannot be calculated by adding these together (the probability would be in the range 0 to 1 and the harm could be in dollars).
B. INCORRECT – Risk is determined by considering a combination of a likelihood and an impact. This definition only considers likelihood and chance (both forms of probability) with no consideration of the impact (or harm).
C. CORRECT – As described in the syllabus (5.5.1).
D. INCORRECT – Risk is determined by considering a combination of a likelihood and an impact. This definition only considers hazards and losses (a hazard is a bad event, similar to a risk, while loss is a form of impact) with no consideration of the likelihood (or probability).
Which of the following is MOST likely to be an example of a PRODUCT risk?
-
A. The expected security features may not be supported by the system architecture
-
B. The developers may not have time to fix all the defects found by the test team
-
C. The test cases may not provide full coverage of the specified requirements
-
D. The performance test environment may not be ready before the system is due for delivery
Justification
A. CORRECT – If the expected security features are not supported by the system architecture, then the system could be seriously flawed. As the system being produced is the problem here, it is a product risk.
B. INCORRECT – If the developers run over budget, or run out of time, that is a problem with the running of the project – it is a project risk.
C. INCORRECT – If the test cases do not provide full coverage of the requirements, this means the testing may not fulfil the requirements of the test plan – it is a project risk.
D. INCORRECT – If the test environment is not ready, this means the testing may not be done, or it may have to be done on a different environment and it is impacting how the project is run – it is a project risk.
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be an example of product risk analysis CORRECTLY influencing the testing?
-
A. The potential impact of security flaws has been identified as being particularly high, so security testing has been prioritized ahead of some other testing activities
-
B. Testing has found the quality of the network module to be higher than expected, so additional testing will now be performed in that area
-
C. The users had problems with the user interface of the previous system, so additional usability testing is planned for the replacement system
-
D. The time needed to load web pages is crucial to the success of the new website, so an expert in performance testing has been employed for this project
Justification
A. INCORRECT – As we are told security flaws have a particularly high impact, their risk level will be higher, and thus we have prioritized the security testing ahead of some other testing. Thus, product risk analysis has influenced the testing.
B. CORRECT – As less defects than expected have been found in the network module, the perceived risk in this area should be lower, and so less testing should be focused on this area, NOT additional testing. Thus, product risk analysis has NOT CORRECTLY influenced the testing in this situation.
C. INCORRECT – Because the users had problems with the user interface of the previous system, there is now heightened awareness of the risk associated with the user interface, which has resulted in additional usability testing being planned. Thus, product risk analysis has influenced the thoroughness and scope of testing.
D. INCORRECT – As the time needed to load web pages has been identified as crucial to the success of the new website, the performance of the website should be considered a risk, and the employment of an expert in performance testing helps to mitigate this risk. Thus, product risk analysis has influenced the testing.
You are performing system testing of a train booking system and have found that occasionally the system reports that there are no available trains when you believe that there should be, based on the test cases you have run. You have provided the development manager with a summary of the defect and the version of the system you are testing. The developers recognize the urgency of the defect and are now waiting for you to provide more details so that they can fix it.
Given the following pieces of information:
-
Degree of impact (severity) of the defect
-
Identification of the test item
-
Details of the test environment
-
Urgency/priority to fix
-
Actual results
-
Reference to test case specification
Apart from the description of the defect, which includes a database dump and screenshots, which of the pieces of information would be MOST useful to include in the initial defect report?
A. 1, 2, 6
B. 1, 4, 5, 6
C. 2, 3, 4, 5
D. 3, 5, 6
Justification
Considering each of the pieces of information:
-
Degree of impact (severity) of the defect – the developers are already aware of the problem and are waiting to fix it, so this is a less important piece of information.
-
Identification of the test item – as the developers are already aware of the problem and you are performing system testing, and you have already provided the version of the system you are testing you can assume they know the item that was being tested, so this is a less important piece of information.
-
Details of the test environment – the set-up of the test environment may have a noticeable effect on the test results, and detailed information should be provided, so this is an important piece of information.
-
Urgency/priority to fix – the developers are already aware of the problem and are waiting to fix it, so this is a less important piece of information.
-
Actual results – the actual results may well help the developers to determine what is going wrong with the system, so this is an important piece of information.
-
Reference to test case specification – this will show the developers the tests you ran, including the test inputs that caused the system to fail (and expected results), so this is an important piece of information.
Thus, option D is CORRECT.
Given the following test activities and test tools:
-
Performance measurement and dynamic analysis
-
Test execution and logging
-
Management of testing and testware
-
Test design
a. Requirements coverage tools
b. Dynamic analysis tools
c. Test data preparation tools
d. Defect management tools
Which of the following BEST matches the activities and tools?
A. 1 – b, 2 – c, 3 – d, 4 – a
B. 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c, 4 – d
C. 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – d, 4 – c
D. 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – d, 4 – c
Justification
The correct pairings of test activities and test tools are, per syllabus (6.1.1):
-
Performance measurement and dynamic analysis – (b) Dynamic analysis tools
-
Test execution and logging – (a) Requirements coverage tools
-
Management of testing and testware – (d) Defect management tools
-
Test design – (c) Test data preparation tools
Thus, option C is CORRECT.
Which of the following is MOST likely to be used as a reason for using a pilot project to introduce a tool into an organization?
-
A. The need to evaluate how the tool fits with existing processes and practices, and determining what would need to change
-
B. The need to evaluate the test automation skills and training, mentoring and coaching needs of the testers who will use the tool
-
C. The need to evaluate whether the tool provides the required functionality and does not duplicate existing test tools
-
D. The need to evaluate the tool vendor in terms of the training and other support they provide
Justification
A. CORRECT – As per syllabus (6.2.2).
B. INCORRECT – The evaluation of the test automation skills and training, mentoring and coaching needs of the testers who will use the tool should have been performed as part of the tool selection activity, as per syllabus (6.2.1).
C. INCORRECT – The decision on whether the tool provides the required functionality and does not duplicate existing tools should have been performed as part of the tool selection activity, as per syllabus (6.2.1).
D. INCORRECT – The evaluation of the tool vendor in terms of the training and other support they provide should have been performed as part of the tool selection activity, as per syllabus (6.2.1).